DIMM SOCKET (Dual In-line Memory Module Socket) is a type of socket or slot used to install and connect memory modules, typically found in computer systems such as desktops, workstations, and servers. DIMM is a standard packaging form for memory modules, offering higher memory capacity and performance compared to traditional SIMM (Single In-line Memory Module).
DIMM emerged after the introduction of the Pentium CPU, providing a new type of memory module. DIMM provides a 64-bit data channel, allowing for single-channel use on Pentium motherboards. It has 168 pins, hence referred to as 168-pin memory modules. It is longer than SIMM slots and supports new 168-pin EDO-DRAM memory.
In general, personal computers use dual-channel memory, with each channel having a 64-bit width and supporting two DIMMs per channel, resulting in a total of four DIMM slots. Servers use Registered RAM, allowing each channel to support multiple DIMMs.
Here are some important points about DIMM SOCKET:
- Installation of Memory: DIMM SOCKET is where memory modules (RAM) are installed. These modules contain random access memory used to store and provide quick access to data for the computer processor (CPU).
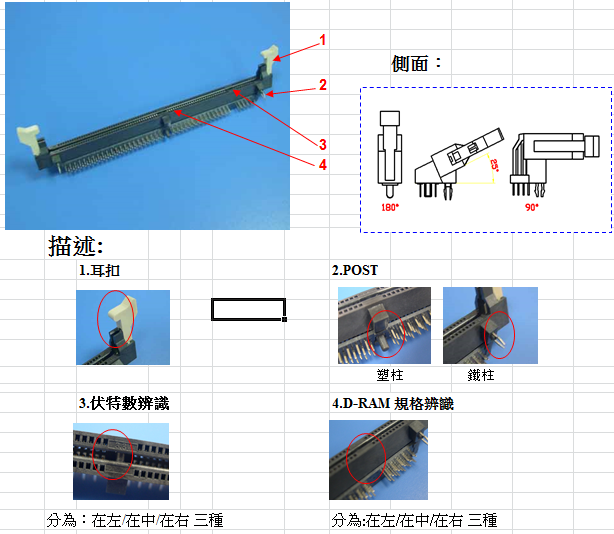
- Number and Type of Slots: Different computer systems have different numbers and types of DIMM SOCKETS, typically depending on the design of the motherboard.
- Memory Capacity Support: The number and type of DIMM SOCKETS will affect the total memory capacity supported by the computer system. The number and specifications of slots will limit the number and capacity of memory modules you can install.
Installation Method
Typically, you gently insert the memory module into the DIMM SOCKET and then press down to ensure a good connection. This is a relatively simple operation but requires care to avoid damaging the socket or memory module.
DIMM SOCKETS are critical components for installing memory modules in computer systems, influencing system performance and memory capacity. Understanding the number and specifications of DIMM SOCKETS is important when upgrading or configuring computers.
Servers use Registered RAM, allowing each channel to support multiple DIMMs. The operating voltage of memory chips suitable for DIMMs is generally 3.3V (except for 168-pin memory modules using EDO RAM memory chips), and the operating voltage for memory chips suitable for SIMMs is generally 5V (using EDO RAM or FBRAM memory chips), and the two cannot be mixed.